As an important heat dissipation device in the industrial field, the transmission mode of the cooling tower fan has an important impact on the operating efficiency and stability of the equipment. There are three transmission modes for cooling tower fans: direct drive, belt drive and gear drive. Each mode has its own characteristics and is suitable for different scenarios and needs. This article will introduce the three transmission modes of cooling tower fans in detail to help readers better understand and choose the transmission mode that suits their needs.
1. Direct drive
Direct drive is a simple cooling tower fan drive method, usually driven by a motor to directly drive the fan blades to rotate. This drive method has a simple structure, easy installation and low maintenance cost. Since the motor is directly connected to the fan, the transmission efficiency is high, which is suitable for small cooling towers or occasions with high transmission efficiency requirements. However, the direct drive method also has some disadvantages, such as high noise, and it is difficult to isolate and repair the motor and fan when they fail. At present, some manufacturers have also developed products that use permanent magnet synchronous motors for direct drive, which have good energy saving performance, but the cost is relatively high.
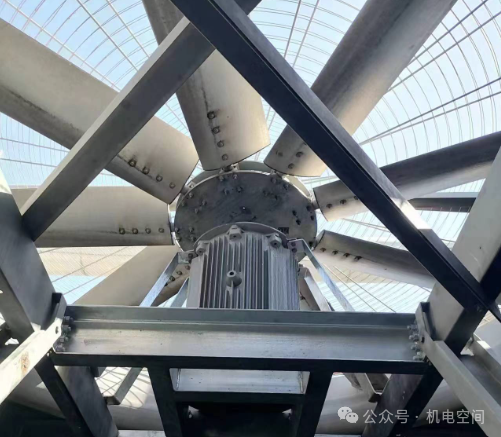

2. Belt drive
Belt drive is a common way of cooling tower fan drive. It drives the pulley through the motor, and then transmits power to the fan blades through the belt. This transmission method can achieve the isolation of the motor and the fan, which is convenient for inspection and maintenance. At the same time, the belt drive has a certain buffering effect, which can reduce vibration and noise. However, belt drive also has some disadvantages, such as low transmission efficiency, and the belt needs to be replaced and maintained regularly, which increases the operating cost.
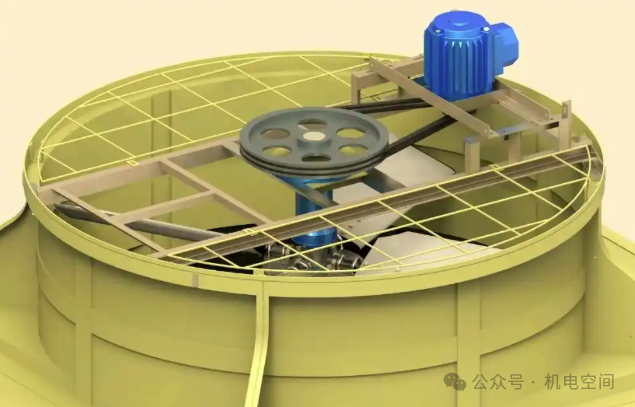
3. Gear drive
Gear drive is a more accurate and efficient type of cooling tower fan drive. It drives the gearbox through the motor, and then the gearbox transmits the power to the fan blades. This drive mode has high transmission efficiency and stability, and is suitable for large cooling towers or occasions with high transmission performance requirements. At the same time, gear drive can also realize speed change and reverse function, which improves the flexibility and adaptability of the equipment. However, the structure of the gear drive mode is relatively complex, and the installation and maintenance costs are high.

In summary, there are three transmission modes for cooling tower fans: direct drive, belt drive, and gear drive. When choosing a transmission mode, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as the size of the equipment, application scenarios, and cost and maintenance requirements. Different transmission modes have their own advantages and disadvantages and applicable scopes. Correctly selecting a suitable transmission mode will help improve the operating efficiency and stability of the cooling tower.
When choosing a cooling tower fan transmission mode, you also need to pay attention to the following points: First, ensure that the transmission mode can meet the heat dissipation requirements of the equipment and ensure the cooling effect; second, consider the reliability and stability of the transmission mode to ensure that the equipment can operate stably for a long time; finally, consider the maintenance cost and convenience of the transmission mode to reduce operating costs and improve the efficiency of equipment use.
Selection suggestions: Belt drive can be selected for general use, which is safe and reliable; high-efficiency machine rooms and other places with high energy-saving requirements and sufficient budgets can consider using permanent magnet synchronous motor direct-drive cooling towers; gear transmission is used with caution due to its high failure rate and difficulty in maintenance. If used, it is recommended to use foreign or joint venture brand products.
 En
En
 عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体

